Publishing Npm package to GitHub Packages
GitHub has integrated the GitHub Packages feature, currently providing package management tools for Npm, Docker, Maven, NuGet, and RubyGems, allowing open-source packages to be managed through GitHub. This article mainly introduces the process of publishing an Npm package using GitHub Packages.
Publishing
First, it is necessary to create a package.json file, which can be generated based on prompts using the npm init command.
Here is an example of a completed package.json file. It is essential to pay attention to the configuration of the name field, publishConfig field, and repository field. When publishing packages to GitHub Packages, they belong to a scope, so the name field should be in the form of @username/package-name. The publishConfig field is a required and fixed-value field for publishing to GitHub Packages. The repository field must specify the repository URL. Multiple packages can be published to a single repository, as shown in this example: https://github.com/WindrunnerMax/Asse/packages/292805.
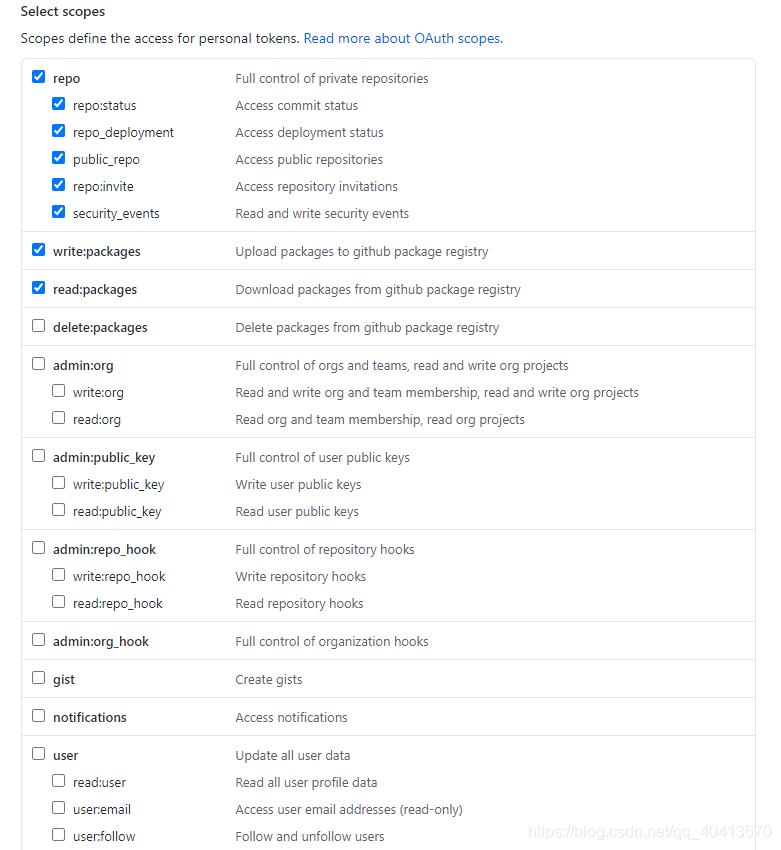
Next, authorization is required. First, apply for a Token in GitHub by navigating to user - setting - Developer settings - Personal access tokens - Generate new token, and generate a Token for publishing Npm packages. When selecting permissions, the following permissions are mandatory:
Next, add the Token to ~/.npmrc. For Windows users, the path is C://users/current-user.
Alternatively, use the npm login command for authorization. Note that the username should be in all lowercase, and the input for the Token will be in the form of a password and will not be displayed.
Then, add a ~/.npmrc file with the following configuration to the root directory of the project.
Finally, the package can be published using the npm publish command.
Installation
It should be noted that whether it's the release package or the installation package, authorization is required. This involves generating the 'Token' mentioned above as well as the configuration process. Otherwise, the specified package cannot be installed. Taking my published package as an example, execute the installation.
If installing Npm packages from GitHub is very slow, consider configuring a proxy. Similarly, add the configuration to the ~/.npmrc file.
